Dow Jones Components: Investment Insights
Unlock the secrets behind Dow Jones components—discover which blue-chip stocks shape the US market and how to invest smarter with expert insights, tips, and strategies.

Introduction
Whether you're new to stock investing or have years of experience, one question surfaces time and again: "How do I choose reliable stocks in the U.S. market?" The challenge is real. With thousands of options—each promising profitability—figuring out where to begin can be overwhelming.
One approach is to decode the underlying forces that drive the American stock market. This is where major indexes come into play. Of these, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (often simply called "the Dow") is among the most widely followed benchmarks. For over a century, its performance has served as a bellwether for broader U.S. economic sentiment and market trends.
Understanding what moves the Dow means looking at its components—the select group of companies whose performance directly shapes the index. These are not just household names, but industry leaders like Apple, Microsoft, and Johnson & Johnson. Recognizing which businesses dominate the Dow, and how their fortunes rise or fall, can help retail investors anticipate sectors or trends likely to outperform.
Knowing the ins and outs of the Dow’s components isn’t just for experts. Even beginner investors can benefit by tracing how changes in, say, Goldman Sachs or Procter & Gamble impact the index. These insights become practical investment guidelines—whether you’re considering buying ETFs like SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF Trust (DIA) or cherry-picking stocks for your portfolio based on their Dow membership.
This article breaks down the essentials: what Dow Jones component stocks are, why they matter for anyone investing in the U.S. market, and how learning their characteristics provides actionable investment strategies. We'll also present a complete, up-to-date list of all Dow components, along with commentary on each—helping you invest confidently with context and clarity.
Understanding Dow Jones Components & Their Importance
What Are Dow Jones Components and Related Terms?
Understanding the foundational elements of the US stock market often begins with the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). The DJIA is one of the most recognized stock market indices worldwide, tracking the performance of 30 large, publicly traded US companies renowned for their stability and consistent earnings.
These companies, commonly known as Dow Jones components, are handpicked to represent various sectors of the US economy. The shares of these companies—often called Dow Jones stocks—are traded on major US stock exchanges, including the NYSE and NASDAQ. Examples of current Dow Jones components include Apple Inc., The Coca-Cola Company, Boeing, and Goldman Sachs. These are not only household names but also industry leaders whose performance shapes broader market sentiment.
In financial circles, you may hear terms like "Dow Jones index companies"—referring specifically to the 30 organizations that make up the DJIA. Because these companies have significant market capitalization and strong track records, their collective performance often sets the tone for the entire market. For instance, after Apple joined the DJIA in 2015, its vast influence in consumer electronics and technology brought the index even more attention from global investors.
Why Do Dow Jones Components Matter?
The companies selected for the DJIA aren’t arbitrary—they are industry titans chosen to represent nearly every major sector of the economy. Fluctuations in the index can signal broader economic health or concern. For example, when the DJIA fell sharply in March 2020 due to pandemic-related uncertainty, it reflected anxiety across sectors like finance, travel, and manufacturing.
The DJIA also serves as a key benchmark for financial products such as mutual funds and ETFs. Fund managers frequently compare their performance against the DJIA, and some funds are even designed to mimic the index's returns. For example, the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF Trust (DIA) lets investors gain exposure to all 30 companies in the index in a single investment, offering a diversified approach for portfolio management.
A strong performance by Dow Jones components attracts attention from global investors, influencing retirement portfolios and international funds. During periods of robust growth from companies like Microsoft or Johnson & Johnson, overseas investors often funnel more funds into US equities, aiming to benefit from the comparatively stable earnings illustrated by the DJIA. For a deeper dive into these trends, see the full explanation of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA).
Who Benefits from Understanding Dow Jones Components?
Recognizing how the DJIA operates can be beneficial for various types of investors and learners. Retail investors who prioritize stability or seek blue-chip stocks often use Dow Jones components as a starting point for their portfolios. These stocks are typically seen as reliable, especially for long-term investment strategies aimed at steady growth and dividend income.
Beginner investors may rely on Dow Jones stocks to build foundational knowledge about the market, learning how established leaders like Procter & Gamble and Home Depot weather economic cycles. Meanwhile, mutual fund investors frequently track the DJIA to align their strategies more closely with market movements. For instance, when the DJIA trends upward, many mutual funds adjust allocations to maintain their performance metrics.
Individuals interested in strengthening their financial literacy, including those following both US and Indian markets, also benefit from understanding these components. By tracking how indices like the DJIA move in relation to similar indices abroad, such as India's Sensex, investors gain global insights and make more informed decisions about diversifying their portfolios.
Dow Jones Components: List & In-Depth Reviews
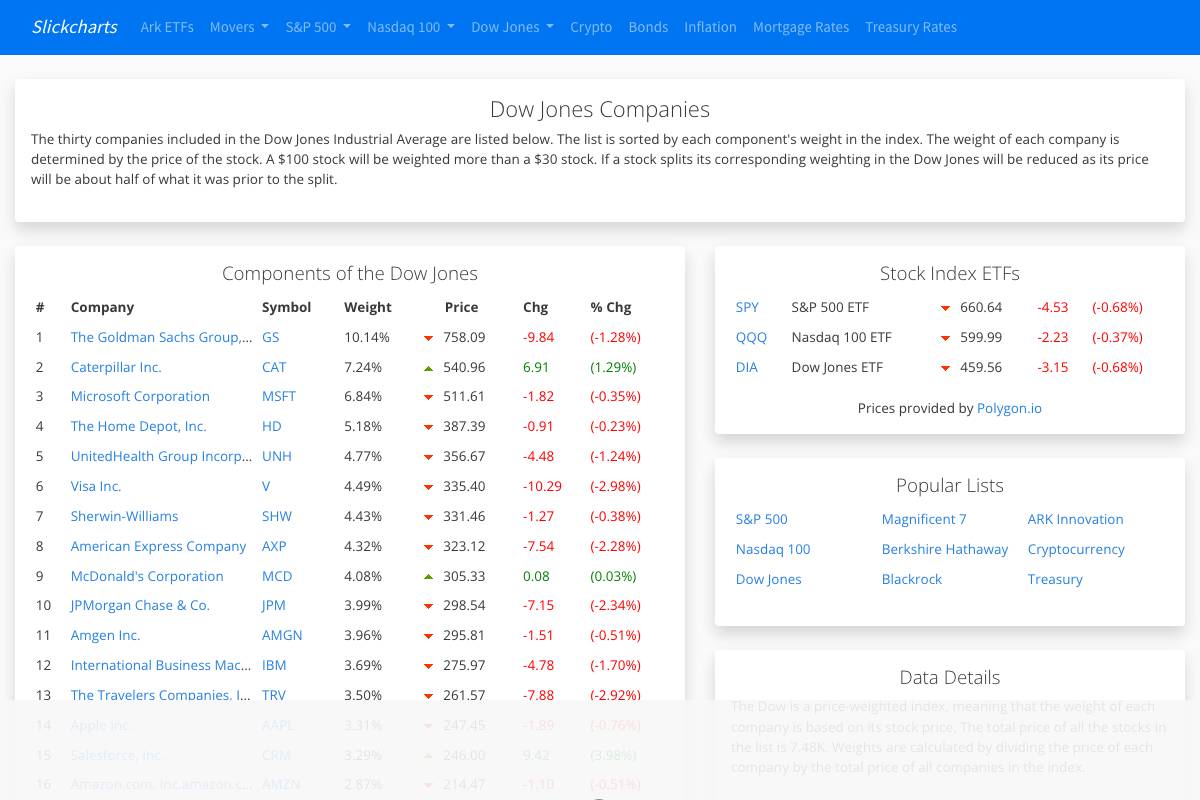
Dow Jones Components: List & In-Depth Reviews
The Dow Jones Industrial Average features 30 prominent companies representing various sectors, providing investors with diversified, blue-chip exposure. Each component holds significant weight, and understanding the strengths, technical requirements, and investment case for these companies is crucial for optimal portfolio decisions. Below, explore some of the most influential names in the index, including in-depth reviews and actionable insights for each.
Apple Inc. (AAPL)
Apple Inc. is a household name, leading the tech sector with relentless innovation. As the maker of the iPhone, iPad, and Mac, Apple’s global influence remains unmatched. It's an appealing option for growth-focused investors and technology enthusiasts alike, backed by a reputation for delivering groundbreaking devices and services.
Trading Apple is accessible via the NASDAQ, using any standard brokerage account or mobile trading app such as Fidelity, E*TRADE, or Robinhood. Investors often benefit from high liquidity and small bid-ask spreads, making it a top choice for both beginners and experienced traders.
Apple's market capitalization exceeded $2.7 trillion in 2023, and its product launches frequently set industry standards. The company’s dominance in consumer electronics is complemented by a robust services division, which contributed nearly $80 billion in revenue in the same year. Apple pays consistent dividends, a rarity for growth tech stocks, and is widely favored for its brand loyalty and financial resilience.
Key Features
- Consistent dividend payouts and strong cash reserves
- High liquidity and trading volume
- Leading R&D investment, with innovations like Apple Silicon chips
- Fractional share availability through platforms like Schwab and Robinhood
Pros
- Globally recognized brand and customer base
- Stable profitability; over $100 billion in annual net income (2022)
- Diversified revenue streams: devices, services, wearables
Cons
- High valuation ratios; P/E often above S&P 500 average
- Revenue heavily tied to iPhone sales (over 50%)
Most brokerages offer fractional shares, enabling investors to start with as little as $1. User sentiment shows Apple considered a "core holding" in many U.S. portfolios, regularly praised for stability and criticized for premium stock pricing.
The Coca-Cola Company (KO)
The Coca-Cola Company represents longevity and reliability in the beverage sector. With a brand portfolio spanning Sprite, Fanta, and Schweppes in addition to its flagship soft drink, it appeals to those seeking dividend stability and defensive positioning.
Coca-Cola trades on the NYSE and is available through any major brokerage. The company’s international reach is vast, distributing products in over 200 countries. It has consistently raised dividends for over 60 consecutive years, earning a spot on the "Dividend Aristocrats" list.
For ESG-conscious investors, Coca-Cola's sustainability initiatives are relevant, but environmental concerns persist, prompting mixed reactions. Its revenue growth is modest compared to technology companies, yet its defensive nature is appealing—Coca-Cola maintained stable profits through periods like the 2008 financial crisis.
Key Features
- Over a century of operational history and brand power
- Quarterly dividend payouts (current yield ~3%)
- Wide international presence and product diversification
Pros
- Low share price volatility
- Strong recession resistance
- Shareholder-friendly payout policy
Cons
- Slower potential for capital growth
- Ongoing ESG and plastic waste concerns
Fractional shares are supported by platforms like Fidelity, but most brokerages require at least one share per purchase. The stock is welcome in many income-focused portfolios. Dividend investors cite KO’s consistent payments as a top benefit, although some are wary of its limited growth prospects compared to peers like PepsiCo.
Microsoft Corporation (MSFT)
Microsoft is at the forefront of cloud computing, software, and enterprise solutions, with Azure now the world’s second-largest cloud platform behind Amazon Web Services. Its product suite extends from Windows and Office to Xbox and LinkedIn, attracting a diverse investor base interested in technology, growth, and reliable performance.
There are minimal technical barriers for trading Microsoft, as it lists on NASDAQ and is supported by all mainstream broker apps, including Robinhood, E*TRADE, and TD Ameritrade. Microsoft’s diversified revenues—spanning business software, consumer products, and cloud—reduce reliance on any single sector.
In 2023, Microsoft’s revenue reached $211 billion, with cloud services accounting for nearly $80 billion. Its consistent dividend increases and stock buybacks signal financial health. However, attention to regulatory issues is warranted, especially following major acquisitions like Activision Blizzard in 2023.
Key Features
- Leadership in cloud computing (Azure’s market share ~24% as of 2023)
- Recurring revenue via Microsoft 365 subscriptions
- Consistent dividend increases for over a decade
- AI and gaming growth vectors (e.g., ChatGPT integration, Xbox Game Pass)
Pros
- Diversified product portfolio with high-margin services
- Strong balance sheet and steady cash flows
- Table-stake holding for institutional and retirement portfolios
Cons
- Faces aggressive competition in cloud (Amazon, Google)
- Subject to increasing antitrust scrutiny
Microsoft shares can be purchased in full or fractional units. The stock remains heavily favored by growth and income investors alike, with high praise for its resilience and innovation—though some suggest its recent P/E ratios make timing a consideration.
Investment Recommendations: Picking the Best Dow Jones Stocks for You
Choosing the right stocks from the Dow Jones Industrial Average involves more than just scanning ticker symbols; it requires aligning your investments with your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. The Dow 30 index is composed of large, stable companies spanning various sectors, providing a rich field for both conservative and growth-oriented investors. Reviewing the latest performance of Dow 30 stocks is a practical starting point for narrowing your options.
For Consistent Dividends and Low Volatility
If your priority is dependable returns with limited price swings, focus on established consumer brands with a strong dividend history. Coca-Cola (KO) and Johnson & Johnson (JNJ) are classic examples. Both companies have increased their dividends for over 50 consecutive years, earning them a spot among the elite Dividend Aristocrats.
Coca-Cola offers a dividend yield typically ranging between 2.5% and 3.5%, while Johnson & Johnson boasts a reputation for weathering market downturns due to its diversified healthcare portfolio. For instance, KO provided steady returns even during market pullbacks in 2020.
For Innovation-Led Growth
Investors seeking higher growth should consider tech giants like Apple (AAPL) and Microsoft (MSFT). These companies dominate in consumer technology and cloud services, generating impressive earnings and driving much of the overall index's gains.
In 2023, Apple and Microsoft together accounted for over 15% of the Dow’s total market capitalization, with Apple consistently delivering year-over-year revenue growth and MSFT leading in cloud infrastructure via Azure. Such leaders demonstrate the value of innovation-driven investments within the Dow universe.
For Sector Diversification
A balanced approach aims for exposure across different sectors to manage risk and capture broader opportunities. Including companies like Visa (financials), UnitedHealth Group (healthcare), and Honeywell (industrials) helps investors diversify beyond consumer and technology segments.
This mix lets you tap into trends such as digital payments growth (Visa), healthcare demand (UnitedHealth), and industrial automation (Honeywell), ensuring your portfolio isn’t overly exposed to one industry’s ups and downs.
For Beginners or Mutual Fund Investors
If you’re new to stock picking or prefer a hands-off approach, consider index funds or ETFs that mirror the performance of the entire Dow Jones, like the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF Trust (DIA). These funds automatically spread investments across all 30 components, reducing individual stock risk.
For example, an investment in DIA allows you to benefit from the performance of all blue-chip Dow companies, letting you ride market trends without frequent trading or active management.
For ESG-Focused Strategies
Responsible investing is becoming increasingly important, and many Dow components now publish detailed sustainability and corporate governance reports. Before selecting stocks, review each company’s ESG disclosures—for example, Microsoft has committed to becoming carbon negative by 2030, while Johnson & Johnson reports extensively on product safety and access to healthcare.
Evaluating these ESG factors ensures your investments align with your values while potentially mitigating risks associated with environmental or social controversies.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I invest in all Dow Jones stocks at once?
Building a diversified portfolio can be complex for individuals, especially when trying to cover all 30 blue-chip companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). Fortunately, there are streamlined ways to access the entire index through a single investment, which reduces both effort and risk.
For most investors, buying an ETF such as the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF Trust (DIA) is the most practical route. The DIA ETF comprises all the Dow components, with portfolio weights matched to the index itself. Mutual funds, like the Fidelity Dow Jones Industrial Average Index Fund, offer similar exposure but sometimes with different fee structures. This method provides instant diversification and reflects the overall performance of major U.S. companies like Apple, Boeing, and Johnson & Johnson in a single purchase.
2. What’s the easiest way for a beginner to track Dow Jones performance?
Keeping tabs on the DJIA doesn't require sophisticated software or market expertise. Many free resources exist that are beginner-friendly and provide real-time data and historical context.
Finance apps such as Yahoo Finance, CNBC, and Google Finance allow users to monitor the Dow Jones index, create watchlists, and view interactive charts. Brokerage platforms like Robinhood and Fidelity also provide DJIA tracking features with optional news alerts. For instance, Robinhood’s dashboard shows current index value, constituent changes, and historical performance in a user-friendly format. Most of these tools require no investment to use, making them accessible for anyone starting their market journey.
3. How often do Dow Jones components change?
The Dow Jones Index is renowned for its stability, but it's not immune to change. Components are reconsidered when the U.S. economy evolves, major corporate actions occur, or companies falter significantly.
Component adjustments are infrequent, often occurring just every few years. For example, in August 2020, companies like ExxonMobil and Pfizer were replaced by Salesforce and Amgen, reflecting shifts in economic sectors. Such changes typically respond to market capitalization trends, mergers, or sustained underperformance. These updates preserve the relevance of the index in representing the U.S. industrial landscape.
4. Are Dow Jones stocks good for short-term trading?
While Dow Jones stocks are pillars of the U.S. economy and offer reliable long-term growth, their relatively low volatility may not appeal to active short-term traders. The index is comprised mainly of established, large-cap companies, which tend to have predictable earnings and modest price swings.
For instance, an investor seeking rapid gains might find more opportunity within technology or biotech sectors—companies like Tesla or Moderna, which often exhibit larger price movements, are not part of the Dow. However, traders focused on options or momentum strategies sometimes leverage Dow ETFs to capture short-term moves around earnings reports or macroeconomic announcements.
5. How do these US stocks impact Indian investors?
Many DJIA companies have an extensive global footprint, making their performance relevant to international investors, including those in India. Their earnings and business prospects often reflect trends beyond the U.S. borders.
For example, Apple, which is part of the Dow, sources manufacturing from and sells products in India. Any shifts in demand in the Indian market can affect its global financials and stock price. Similarly, Johnson & Johnson has a large healthcare business in India, influencing accessibility and pricing of its medications and devices. As a result, Indian investors in US markets or mutual funds tracking the DJIA should pay attention to both local and American economic indicators for a nuanced investment strategy.